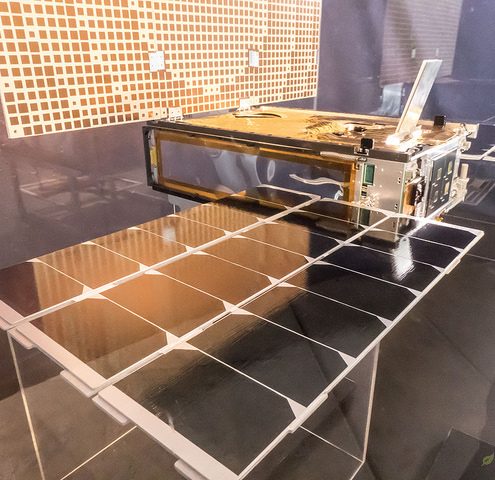
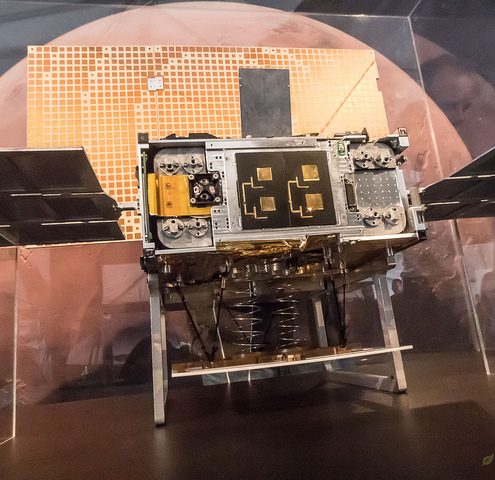
On November 26, 2018, NASA’s InSight lander arrived at Mars, our neighboring red planet, after a nearly seven month journey through deep space, but it didn’t travel alone. Twin satellites, collectively named “Mars Cube One” (MarCO), launched aboard the same Atlas V rocket on May 5, 2018 and followed closely behind. The MarCO mission was flown with InSight as a demonstration of communication and navigation capabilities for satellites in the CubeSat category. Each device measures about 14.5 inches by 9.5 inches, forming a six-unit CubeSat, and their mission represents a new chapter in citizen space exploration.

What are CubeSats?
CubeSats are tiny satellites meeting specific dimensions (multiples of 10 cm x 10 cm x 10 cm, 1 kg) and generally built with off-the-shelf components. They originated as an attempt to provide affordable access to space for the university science community and have since expanded into a multitude of other civilian projects, both non-profit and commercial. NASA in particular has worked to formalize the requirements for these types of satellite missions, even providing guides to assist with team efforts. CubeSat projects to date have included things like orbital telescopes, testing propulsion concepts (ion engines, solar sails), radio transmissions, and music via sonification.
Considering the average cost for a standard satellite is in the millions of dollars for both development and launch, the $50,000 or so the average CubeSat costs to build and launch is practically miniscule in comparison. Even projects with higher budget requirements can find funding readily enough, meaning that space exploration is no longer limited to large government projects and multimillion dollar corporate products. Now, with MarCO’s successful trip to Mars, Earth orbit is no longer the limitation for these small satellites. With companies like SpaceX pushing for multiplanetary habitation, enthusiastic citizen space explorers could perhaps assist with the scientific and technological research that will be needed to get us there.
The Mars Cube One Mission
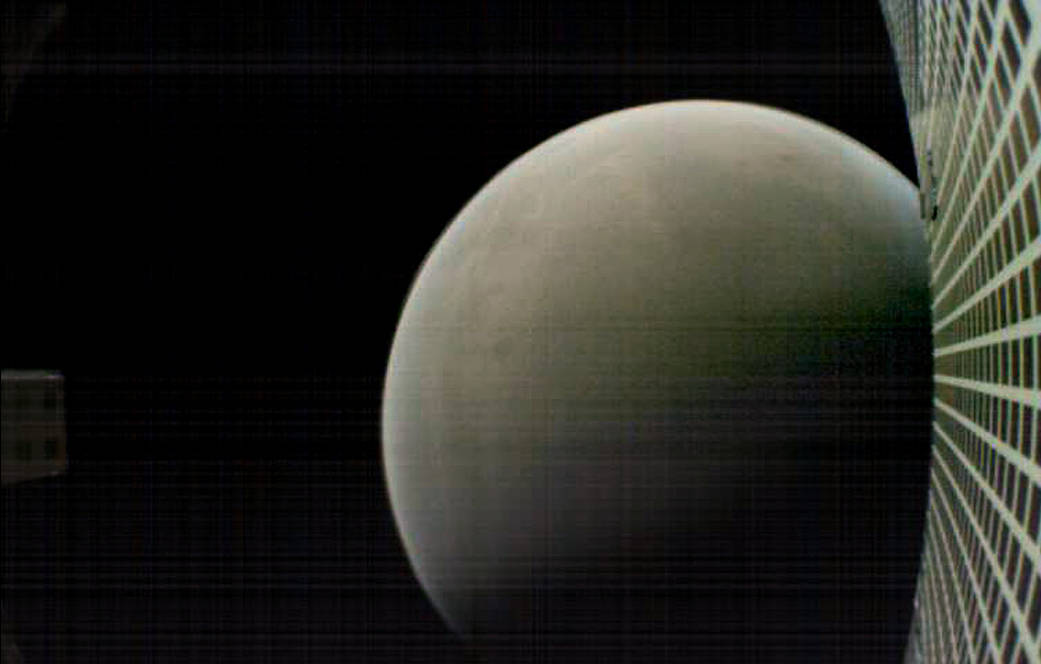
MarCO’s primary mission was to demonstrate the ability to relay status information from the InSight lander to Earth as the craft descended onto the Martian surface. To accomplish this, the CubeSats transmitted signals to NASA’s already orbiting Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter which then forwarded the information to Earth. The successful transmissions provided scientists with information on InSight’s status much faster than would have otherwise been available due to orbital limitations. Additionally, the twin satellites used their own navigational systems to guide their journey to Mars, further advancing the cause of tiny satellites in deep space.

The success of the MarCO mission doesn’t just mean good news for future Mars citizen explorers. With the Moon back in the spotlight for exploratory missions and the growing interest in close, deep space targets like Venus, a wealth of data may be the near future arising from CubeSat projects. Where money was once a major inhibitor to space science projects, MarCO’s CubeSats have left the door wide open for the next generation of exploration to begin.
Watch the below video for more about NASA’s first deep space CubeSats: